Components of HVAC Systems
A well-designed HVAC system is a symphony of various components working together to ensure optimal indoor comfort. Each component serves a specific function, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the system. Let’s explore these key components in detail:
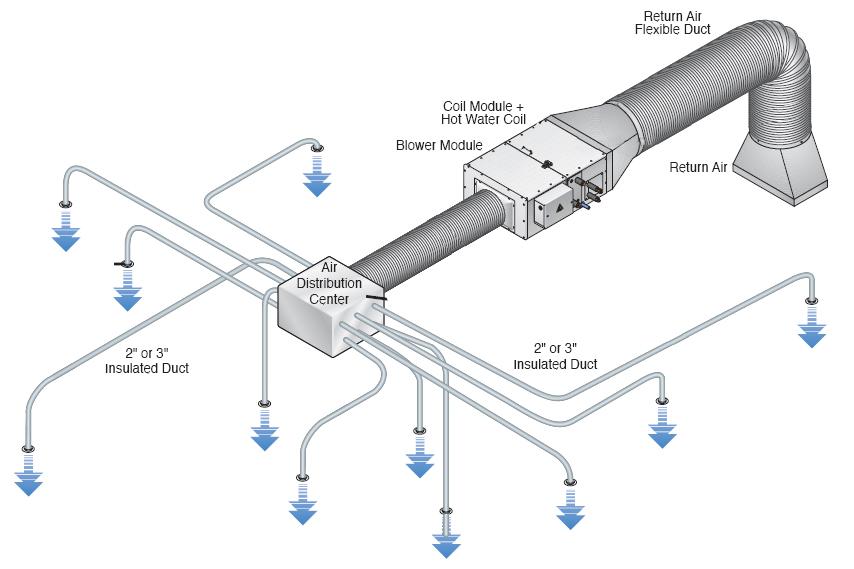
Heating Systems:
- Furnaces:
- Furnaces are central to heating systems and are commonly powered by electricity, natural gas, or oil. They generate heat by burning fuel or using electrical resistance and then distribute the warm air through ductwork to various spaces.
- Boilers:
- Boilers heat water to produce steam or hot water, which is then circulated through radiators or underfloor heating systems. This method is common in residential and commercial applications.
- Heat Pumps:
- Heat pumps are versatile systems that can both heat and cool spaces. They work by transferring heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. Air-source and ground-source heat pumps are two common types.
Ventilation Systems:
- Fans:
- Fans play a crucial role in ventilation by moving air throughout the building. They can be part of the HVAC system or standalone units. Fans are used to distribute conditioned air and ensure proper air circulation.
- Ductwork:
- Ductwork is a network of pipes or channels that transport air throughout the building. Well-designed ductwork is essential for efficient air distribution, and it includes supply ducts that deliver conditioned air and return ducts that bring back air for reconditioning.
- Air Handling Units (AHUs):
- AHUs are devices that condition and circulate air. They typically include a blower, filters, heating or cooling elements, and dampers. AHUs are crucial in maintaining indoor air quality and temperature control.
Air Conditioning Systems:
- Compressors:
- Compressors are the heart of air conditioning systems. They compress refrigerant gases, raising their temperature and pressure. The compressed refrigerant is then circulated through the system to absorb and release heat.
- Evaporators and Condensers:
- Evaporators facilitate the absorption of heat from indoor air, cooling it. Condensers release heat to the outside environment, completing the refrigeration cycle. These components work in tandem to regulate temperature and humidity.
- Thermostatic Expansion Valves (TXVs) and Metering Devices:
- These devices regulate the flow of refrigerant, ensuring that the right amount reaches the evaporator. Proper refrigerant control is essential for efficient and precise temperature control.
Integrated Control Systems:
- Thermostats:
- Thermostats serve as the user interface for HVAC systems, allowing occupants to set desired temperatures. Modern thermostats often include programmable features and connectivity for remote control.
- Sensors:
- Various sensors, such as temperature and humidity sensors, are integrated into HVAC systems to provide real-time data. This information helps the system adapt to changing conditions for improved efficiency.
- Control Panels:
- Centralized control panels manage the overall operation of the HVAC system. They coordinate the activities of different components, optimizing performance and ensuring energy efficiency.
A well-designed and properly maintained HVAC system is essential for creating a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. Understanding the functions of each component allows for efficient operation, effective troubleshooting, and informed decision-making in the design and maintenance of HVAC systems. In the subsequent chapters, we will delve deeper into the operation, design considerations, and maintenance practices associated with these components.

